What is an Exoplanet? Space missions to detect Exoplanets | Methods to detect Exoplanets | About Habitable zone
All planets in the solar system
orbits around the Sun. In the same way many planets orbit their host stars
outside the solar system called as Exoplanets. Our own Milky way galaxy
contains billions of stars in which billions of planets orbiting around them.
We will find these Exoplanets through
1. Ground based observatories
2. Space observatories
From ground based observatories,
it's hard to find an Exoplanet because of
- In day time, Sun blocks most of the light reaching us.
- In night time, it's hard due to the Earth rotation, atmosphere and climatic conditions.
Through ground based
observatories, we have traced out nearly 600 Exoplanets until now. So therefore
the other way to find Exoplanets is through space observatories, but it will
costs huge amount of money. So until now only 9 spacecrafts were launched to
detect Exoplanets. Here is a small brief about each of them.
1. EPOXI - It is organised by
NASA. It didn't detected any Exoplanet. (2005 - 2013)
2. Gaia - It is organised by ESA.
It didn't detected any Exoplanet until now. (2013 - ongoing)
3. ASTERIA - It is organised by
NASA's JPL in collaboration with MIT. It didn't detected any Exoplanet until
now. (2017 - ongoing)
4. CHEOPS - It is organised by
ESA. It didn't detected any Exoplanet until now. (2019 - ongoing)
5. MOST - It is organised by CSA.
It confirmed 1 Exoplanet until now. (2003 - ongoing)
6. SWEEPS - It is organised by
NASA, ESA and Space telescope science institute. It confirmed nearly 16 Exoplanets.
It started in the year 2006 and ended in the same year.
7. COROT - It is organised by
CNES in collaboration with ESA. It confirmed nearly 29 Exoplanets. (2006 -
2012)
8. TESS - It is organised by
NASA. It confirmed nearly 38 Exoplanets until now. (2018 - ongoing)
9. Kepler/K2 - It is one of the
major space telescopes, which is dedicated to detect Exoplanets. It is
organised by NASA. It confirmed nearly 2774 Exoplanets. It explored for a total
of nine years from 2009 to 2018.
 |
| Kepler_space_telescope_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: NASA |
So if we want to know about the Exoplanets
and their existence, we have to mainly depend on the NASA.
There are many ways to find an Exoplanet, but mainly 6 methods were used. They are:
1. Transit Photometry method
2. Radial Velocity method
3. Direct Imaging
4. Gravitational Microlensing
5. Astrometry
6. Timing variations
Other methods used are Phase
curves, Polarimetry, Interferometry, Ellipsoidal variations etc.,
The first Exoplanet was
discovered in the year 1995, named as ‘51 Pegasi b’ also called as ‘Dimidium’ orbiting
around Sun like star called ‘51 Pegasi’.
Does finding an Exoplanet benefit mankind?
Yes, but in very less amount of
profit. Using this information we can estimate the possibility of carbon based
life beyond our solar system.
For example, in our own solar
system life exists only on earth because
- Earth contains planetary surface which supports liquid water to stay on the surface creating atmospheric pressure.
- Earth position is also well balanced to encounter the Sun's radiations.
The planets which are nearer to the
Sun, will face higher radiation leading to increase in temperatures. So there
is very less chances of liquid water to exist.
The planets which are in long
distances from the Sun, will have lower temperatures because of very less
amount of Sunlight reaches surface. So in these planets water will exist in the
form of ice.
So Earth is in the right position
where liquid water can exists. This zone is called Goldilocks zone or habitable
zone.
 |
| Habitable_Zone_Into_the dark_space Image credit: NASA |
- In hotter star, the position of habitable zone is in long distances.
- In cooler star, the position of habitable zone is in near to the star.
- In stars like Sun, the position of habitable zone is in right at the place of earth.
 |
| Habitable_Zone_for_different_stars_Into_the dark_space Image credit: NASA/Kepler mission/Ames Research Center |
Like that of the Earth scientists
discovered 17 exoplanets which are in habitable zone orbiting their host stars
and other 30 exoplanets have chances to be in habitable zone.
In the journey of finding of
Exoplanets, Kepler space telescope helped us the most. It can observe light from
distant stars and planets. To find Exoplanets, it uses a technique called
transit photometry which is simply called transit method. This process will go
on for a total of 2 to 16 hours continuously and scientists will made some
calculations to confirm an Exoplanet.
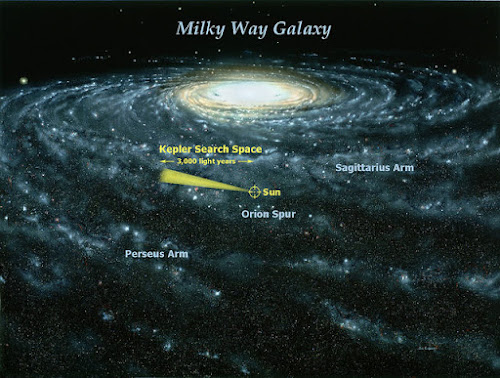 |
| Kepler_research_in_milky_way_Into_the_dark_space Imagr credit: Painting by Jon Lomberg, Kepler mission diagram added by NASA |
How names will be given to Exoplanets?
If a telescope detects any new
celestial object, then the country which organised that telescope can give any
name to that new celestial object under the International Astronomical Union
(IAU). Astronomers belonging to all countries are in the part of IAU.
Let us understand the procedure
with an example.
Assume we found a Exoplanet using
Kepler telescope,
If it detected a new star system
then, star will be given name after Kepler as: Kepler + Number.
Planets around that star: Star
name + lowercase letter (starting with b).
In case of multiple star system,
for star: Kepler + Number + uppercase
letter and for planets around them: Star name + lowercase letter (starting
with b).
 |
| Trappist-1_system_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech |
Share your ideas and thoughts in comment section below.
For more information click here and for updates please follow my site,
Thank you.
Nice one ☝
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteSuperb
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteGood info
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteWow
ReplyDeleteThank you.
Delete