Will Betelgeuse go for supernova? | What will happen if Betelgeuse go for supernova?
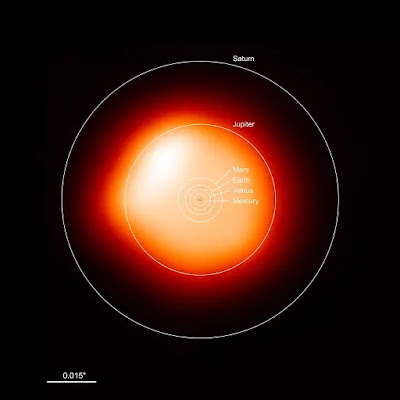
In recent times, Betelgeuse became the one of the hot topics in astronomy. It is usually the 11th brightest star in the night sky and 2nd brightest one in the constellation of Orion. It is classified under the category of red super giant, is a variable star with radius about 617 million kms which is around 10 to 25 times the Sun's mass. If it is in the place of the sun, then it will engulf the orbits of the all terrestrial planets in our solar system and can reach up to the Jupiter's orbit.
 |
| Size_comparison_Betelgeuse_and_the_Sun_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/E. O’Gorman/P. Kervella https://www.eso.org/public/images/potw1726b/ |
It is estimated that it was formed 8 to 8.5 million years ago (quite young star) but it is in its end stages rather than that of Sun which is formed 4.5 billion years ago but still in its middle stages because bigger stars, run out of fuel very fast than that of smaller one's. According to scientists, when compared the size, mass and age of the star it is estimated that it will die in between next 0.1 million years from now.
Since it is a variable star, the brightness of the star changes because of its dimming cycle which is 425 days which indeed means, the radiation pressure and gravity are not well balanced. Between September 2019 and January 2020, it gets dimmed significantly enough to be noticeable with the naked eye. As mentioned earlier, it is the 11th brightest star in the night sky which goes upon to 13th or 14th places when dimming cycle occurs and comes back to 11th place.
 |
| Betelgeuse_before_and_after_dimming_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: ESO/M. Montargès et al https://www.eso.org/public/images/eso2003c/ |
But recently it came down to below 20th place. So some scientists thought that it will go for supernova. Since every star was born from gas & dust clouds starts fusing hydrogen into helium and glows. When a star uses its complete fuel for fusion process then the radiation pressure will decreases leads to its own gravity to compress the star and then explodes which is called a 'supernova'.
Effects to Earth:
Commonly, if a star gone for supernova the shockwaves, gamma rays, dust and high energy radiations will reach up to 50 light years (depend upon the star properties). As betelgeuse was in 650 light years away from us there is no effect on Earth. But if earth was in 50 light years or less, then due to supernova life on earth becomes dead within fraction of seconds. But we can say that if it occurs, it will be the closest supernova ever observed by mankind. Because it is a red super giant and nearer to us. we can watch it from Earth as bright as the moon in the night sky.
In 1054 AD, a supernova called SN 1054 occurred at a distance of 6523 light years away but people on earth watched it for more than 2 years. In the year 1604, a supernova called Kepler's supernova occurred. If Betelgeuse go for supernova then it is brighter than that of two we know. Seeing a star means seeing into the past so we are watching Betelgeuse as it was in 650 years ago. We don't know whether it is exploded or not but only we consider the light when it reaches us.
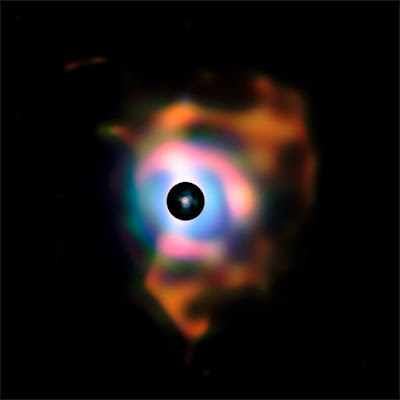 |
| Nebula_around_Betelgeuse_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: ESO/P. Kervella https://www.eso.org/public/images/eso1121a/ |
Recently, the red super giant once again returns back to its brightness levels. As per the research in February this year scientists finally concluded that, Betelgeuse sneezed out a huge cloud of dust which obscured its light for a while which means star isn't about to go for supernova. Since Betelgeuse caught the attention of astronomers last year when it started decreasing its brightness.
If supernova occurs, it is the top astronomical event ever seen by us in our life time. Let's wait...
Share your ideas and thoughts in comment section below.
For more information click here and for updates please follow my site,
Thank you.
Nice one
ReplyDeletethank you
DeleteBlogs with lots of information
ReplyDeletethank you
Delete