The Journey of ISS | Components of ISS | Assembly of ISS | Information about International Space Station
An average satellite weighs between 500 kg to 15 tons and sizes in between 1 metre to 15 metres in length, width and height. Satellites are carried into Earth’s orbit by the help of rockets. ISS has a length of 109 metres, width of 75 metres and height of 20 metres. We can watch the ISS with our naked eye from Earth, when it passes through our night sky. It weighs around 420 tons, which is the highest weighted space craft ever built by humans. As all know, such a type of space crafts are hard to carry into Earth’s orbit by rockets, due to their large weight and size.
Why we need ISS?
In future, humans may colonize other worlds too. For this, humans need to survive in space for a long time. If we survive, we have questions like how health will be affected in space, how medicines will help us in space and more. To answers these questions, humans have to experience a long time journey in space. So, in start of this century scientists got an idea to build a space station in Earth's lower orbit.
In 1984, NASA announced a project called “Space station freedom”. Later, NASA is ready with designs for space station to launch, but it postponed for years due to technical challenges and US government.
Again in 1993, NASA in conjunction with other space agencies started to design space station. Due to the membership of other countries, the name space station freedom changed to “International space station”, in which the main members are NASA, ROSCOSMOS followed by JAXA, CSA and ESA.
Space agencies took several years to construct ISS in space, due to its large size and design. Total assembly of ISS is done in space, by assembling of different components carried by rockets. Space agencies took 13 years to construct ISS in space (from 1998 to 2011). But even now some small parts are being assembled to ISS. Before going through the assembly process, we have to know about docking.
Docking is the connection between two space vehicles. Since 1998, different components are connecting to ISS, so the connecting components must have docking ports. Every space craft must go through docking process to connect with ISS.
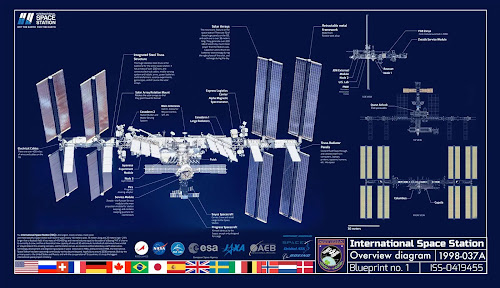
Components of ISS:
ISS consists of,
Solar arrays - Used to store solar energy.
Radiator panels - Releases internal heat from ISS.
Integrated truss structure - It is the backbone for ISS. Integrated truss structure connects all components and parts of ISS.
Pressure modules - It is the home for Astronauts and Cosmonauts in ISS. They can survive here without space suits and major experiments are done here.
ISS consists of two pressure modules,
One belongs to Russia called ‘Russian Orbital Segment’ and other belongs to USA called ‘US Orbital segment’. US orbital segment consists of some components of other countries like Canada, Japan and even some other European countries. These modules helps the ISS to run.
All these modules and components are mainly launched by 3 rockets, called
1. Space shuttle belongs to USA.
2. Proton and
3. Soyuz belongs to Russia.
All the connections in ISS are operated by ground based communications.
 |
| Components_of_ISS_Into_the_dark_space |
Assembly of ISS:
Assembly of ISS has taken several years to construct. Still assembling of some components are going on and will be happening in future also. Due to many components in it, I will discuss them in a table for understanding easily.
| Component/Module | Country/Space agency | Date | Connection | Use/Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zarya | Russia | 20 Nov, 1998 | - | Consists of solar arrays and propulsion systems. 3 docking ports at front and 1 at back |
| Node-1 | US | Dec, 1998 | - | Consists of 6 docking ports. It helps ISS to connect more components |
| Zvezda | Russia | Jul, 2000 | - | Consists of 3 docking ports at front and 1 at back. It is center for Russian Orbital Segment |
| Z1 Truss | US | Oct, 2000 | - | It is a part in Integrated Truss Structure |
| P6 Truss | US | Nov, 2000 | Docked above Z1 Truss | Consists of solar arrays and radiator panels |
| Desting module | US | Feb, 2001 | - | It is US laboratory and research center |
| ESP-1 | - | Mar, 2001 | - | - |
| Canadarm2 | Canada | Apr, 2001 | - | Astronauts and Cosmonauts will operate this arm from inside |
| Quest air lock | US | Jul, 2001 | - | From this Astronauts can enter into space safely by spacesuits (Spacewalk). It helps to repair other components |
| Pirs | Russia | Sep, 2001 | - | It is useful for spacewalk and has 1 docking port |
| S0 Truss | US | Apr, 2002 | Connected to Destiny module | - |
| MBS | Canada | Jun, 2002 | - | - |
| S1 and P1 Truss | US | Oct and Nov, 2000 | Connected to S0 Truss at ends | Consists of radiator panels |
| ESP-2 | - | Jul, 2005 | - | - |
| P3 and P4 Truss | US | Sep, 2006 | - | Consists of solar arrays and radiator panels |
| P5 Truss | US | Dec, 2006 | - | Balacing for remaining Truss |
| S3 and S4 Truss | US | Jun, 2007 | Connected to S1 Truss | - |
| S5 Truss and ESP-3 | US | Aug, 2007 | - | Balancing for remaining Truss |
| Harmony node 2 | US | Oct, 2007 | Connected to Destiny module | Consists of 6 docking ports |
| Columbus module | ESA | Feb, 2008 | Connected to Destiny module | It is Europe laboratory |
| Japanese Logistics module | Japan | Mar, 2008 | - | - |
| Dextre | Canada | Mar, 2008 | Connected to canadarm2 | - |
| Kibo | Japan | May, 2008 | Connected to Destiny module | It is Japan laboratory and have separate robotic arm |
| S6 Truss | US | Mar, 2009 | Connected to S5 Truss | - |
| Japanese Exposed Facility | Japan | Jul, 2009 | Connected to Japan module | - |
| Poisk | Russia | Nov, 2009 | - | - |
| ELC-1 | US | Nov, 2009 | - | It stores hardware and helps ISS to work properly |
| ELC-2 | US | Nov, 2009 | Connected at top of the Truss | - |
| Node 3 | US | Feb, 2010 | Connected to Node 1 | Consists of a room called Cupola, has windows |
| Rassvet | Russia | May, 2010 | - | Helps to store materials and has 1 docking port |
| Leonardo module | US | Feb, 2011 | Connected to node 3 | It helps to store materials and wastage |
| ELC-3 and ELC-4 | US | May and Feb, 2011 | - | It is used for science experiments |
| Beam module | US | Apr, 2016 | - | Consists of upgraded technology |
| IDA-2 | US | Jul, 2016 | - | - |
| IDA-3 | US | Jul, 2019 | - | - |
Since 1998, several modules and components are connected to ISS. It is the largest human made object ever built in space. Until now, more than 120 rockets are launched to ISS and costed nearly 150 billion US dollars for construction and expeditions.
ISS is in the low Earth orbit, above 400 kms from the Earth's surface, orbiting at a velocity of 27,700 kms/hr. It completes one revolution around Earth in 90 minutes and completes 16 revolutions every day. Since 2000, for every 6 months a group of Astronauts and Cosmonauts are visiting ISS. In which the research and experiments in space are done.
ISS is a big step taken by humans to explore and colonize other worlds.
Share your ideas and thoughts in comment section below.
For more information click here and for updates please follow my site,
Thank you.

Nice
ReplyDeleteNice information....👌
ReplyDeleteThank you, share.
DeleteSuperb..... good information 😉
ReplyDeleteThank you, keep sharing.
DeleteVamooooo.....
ReplyDeleteWhat reyyyy
Haha, ok.
DeleteGud work..keep going
ReplyDeleteThank you, keep supporting.
Deletesuperb broooo
ReplyDeleteThank you, share.
DeleteSuper ra hemanth inka baaga chey
ReplyDeleteSure, Thank you.
DeleteGood information 👌
ReplyDeleteThank you.
DeleteGud information.. keep it up...
ReplyDeleteThank you, share.
DeleteExcellent ra 👏👌 well done.
ReplyDeleteThank you.
DeleteGood
ReplyDeleteThank you.
DeleteVery nice
ReplyDeleteThank you.
Delete