Information about Exoplanets | Potentially habitable Exoplanets | Habitable Exoplanets Part-1
(Note: Before reading this article, go through our last
article about Exoplanets. So that you can understand this article easily, click here to open.)
In search of Extrasolar planets, we use both ground based
and space observatories to detect Exoplanets. In which the space observatories like Kepler space
telescope, COROT, TESS, SWEEPS and ground based observatories like HAT, WASP,
HARPS helped us the most.
Different observatories use different kinds of methods to
detect Exoplanets such as Transit Photometry, Radial Velocity, Gravitational
Microlensing, Direct Imaging, etc., In which most of the Exoplanets are
detected by using Transit Photometry and Radial Velocity method.
Most of the successful space observatories like Kepler,
TESS, COROT, SWEEPS and ground based observatories like HAT, WASP are using
Transit Photometry to detect Exoplanets.
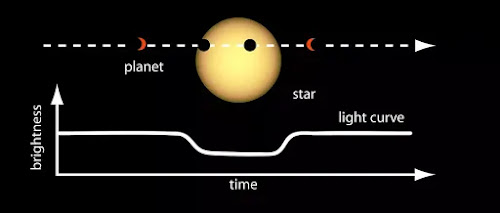
Transit Photometry:
When a planet passes between the observer and star
(transit), it blocks the light reaching us from the star for a certain period
of time. Transit causes the stars to decrease in brightness in very low
amounts.
This was calculated by the chart called 'light curve'. It
indicates the dip in brightness of the star for a while (2to16 hours). This method is not
only used for finding planets, but also used for finding the atmosphere,
temperature and compositions of the planets by observing light from the
planets.
 |
| Transit_method_to_detect_Exoplanets_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: NASA Ames |
According to NASA, 3170 Exoplanets were discovered until now
by using Transit Photometry method.
Let’s discuss about some of the Potentially habitable
Exoplanets, where life can be supported.
Gliese 667 Cc:
It is an Exoplanet located at a distance of 23 light years
away from the Earth in the constellation of Scorpius. It is orbiting around the Gliese
667 C star, a member of triple solar system. It is detected by using the Radial
Velocity method by ESO on 21 November, 2011. It is estimated that, it was
formed 2 billions years ago. It have an orbital period about 28.15 Earth days.
It is 1.54 times the Earth's size and 3.7 times the Earth’s mass. It may have
temperatures about 4°C to 30°C and this allows the higher chances of atmosphere
and life to exist. It has higher chances to have liquid water on the surface.
 |
| Gliese_667_Cc_impression_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: ESO/L. Calçada https://www.eso.org/public/images/eso1214a/ |
Kepler 186 f:
It is an Exoplanet located at a distance of 550 light years away from the Earth. It is the 5th planet orbiting around the Kepler 186 star in
habitable zone. It is detected by Kepler space telescope (uses Transit Photometry to detect Exoplanets) on 17 April, 2014. It have an orbital period
about 130 Earth days. It is 1.1 times the Earth's size and 1.5 times the
Earth's mass. It may have temperatures about -80°C to 10°C, so water exists in
the form of ice. This Exoplanet may have atmosphere and oceans above the
surface.
 |
| Kepler-186f_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: NASA/Ames/SETI Institute/JPL-Caltech |
Proxima Centauri b:
It is an Exoplanet located at a distance of 4.2 light years away from the Earth, orbiting around the Proxima Centauri star in the habitable zone. It
is the nearest Exoplanet to the Earth orbiting in the habitable zone. It is
detected by using Doppler Spectroscopy method by ESO on 24 August, 2016. It
have an orbital period about 11.2 Earth days, meaning all the seasons will
complete in this 11.2 days. It is 1.1 times the Earth's size and 1.3 times the
Earth's mass. It may have temperatures about -40°C to 20°C, so water exists in
the form of ice or liquid. It may have atmosphere and rocky surface.
 |
| Proxima_Centauri_b_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: ESO https://www.eso.org/public/images/ann16056a/ |
HD 40307 g:
It is an Exoplanet located at a distance of 42 light years away from the Earth in the constellation of Pictor. It is orbiting around the HD 40307
star in the habitable zone. It is detected by using Radial Velocity method by
Mikko Tuomi et al on 28 October, 2012. It have an orbital period about 198
Earth days. It is 2.4 times the Earth's size and 7 times the Earth's mass. It
may have atmosphere and chances of existence of life.
 |
| HD_40307_g_Into_the_dark_space By Kaptsov Ruslan - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=44799281 |
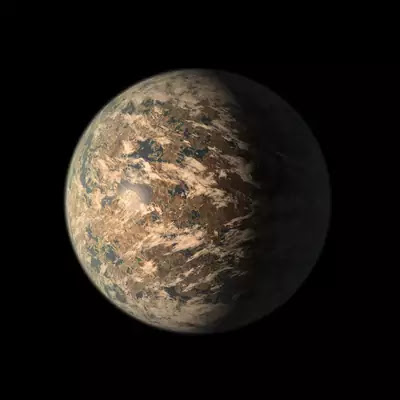
Trappist 1e:
It is an Exoplanet located at a distance of 40 light years away from the Earth. It is orbiting around the Trappist 1 star in the habitable zone. It
is detected by Spitzer space telescope (Transit Photometry) on 22 February,
2017. It have an orbital period about 6.09 Earth days. It is 0.9 times the
Earth's size and 0.7 times the Earth's mass. It may have temperatures about
-48°C to 40°C. Especially, Trappist 1e's radius, mass, density, gravity and
temperature is like that of Earth. So there are higher chances of life to
exist.
 |
| TRAPPIST-1e_Impression_Into_the_dark_space Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech, Cropped from PIA22093: TRAPPIST-1 Planet Lineup |
Share your ideas and thoughts in comment section below.
For more information click here and for updates please follow my site,
Thank you.
interesting bro....i like this theme.....
ReplyDeleteGood information 👌👌👌
ReplyDeleteThank you, share.
DeleteWoww interesting
ReplyDeleteInteresting
ReplyDeleteNyc one
ReplyDeleteThank you.
Delete